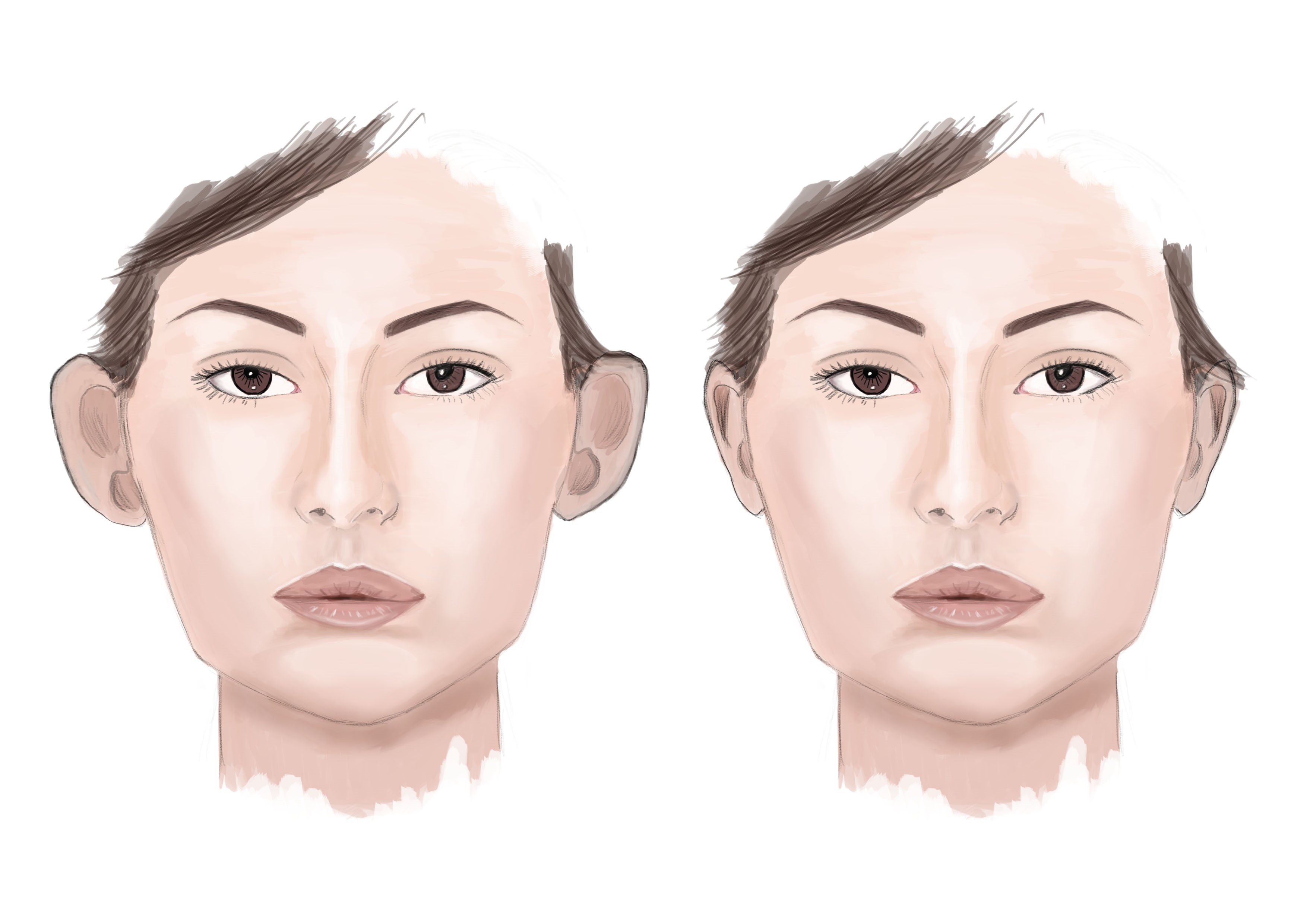
What is Ear Surgery?
Ear surgery, also known as otoplasty, can improve the shape, position or proportion of the ear.
Otoplasty can correct a defect in the ear structure that is present at birth that becomes apparent with development or it can treat misshapen ears caused by injury.
Ear surgery creates a more natural shape, while bringing balance and proportion to the ears and face. Correction of even minor deformities can have profound benefits to appearance and self-esteem.
If protruding or disfigured ears bother you or your child, you may consider plastic surgery.
What ear surgery can treat
- Overly large ears — a condition called macrotia
- Protruding ears occurring on one or both sides in varying degrees — not associated with hearing loss
- Adult dissatisfaction with previous ear surgery
Ear Surgery cost
Otoplasty cost can vary widely. The average cost of otoplasty is AU$3,000.
A surgeon's cost for ear surgery may vary based on his or her experience, the type of procedure used, as well as geographic location.
Many plastic surgeons offer patient financing plans to cover the price of otoplasty, so be sure to ask.
Ear Surgery costs may include:
- Anesthesia fees
- Hospital or surgical facility costs
- Medical tests
- Post-surgery garments
- Prescriptions for medication
- Surgeon's fee
Otoplasty and Health Insurance
Most health insurance plans will not cover elective surgery, related complications or another surgery to revise the appearance of your ears.
Some procedures may be covered by health insurance, particularly when it is performed to relieve medical symptoms or to restore hearing function. Pre-certification is often required for reimbursement or coverage. Be sure to consult with your insurance company in advance of any surgery.
Ear Surgery Candidates
Children who are good candidates for ear surgery are:
- Healthy, without a life-threatening illness or untreated chronic ear infections
- Generally 6 years old, or when a child's ear cartilage is stable enough for correction
- Cooperative and follow instructions well
- Able to communicate their feelings and do not voice objections when surgery is discussed
Teenagers and adults who are good candidates for ear surgery are:
- Healthy individuals who do not have a life-threatening illness or medical conditions that can impair healing
- Individuals with a positive outlook and specific goals in mind for ear surgery
Ear surgery is a highly individualized procedure and you should do it for yourself, not to fulfill someone else's desires or to try to fit any sort of ideal image.
Ear Surgery Recovery
Discomfort immediately following ear surgery is normal and can be controlled with pain medication. There may be an itchy feeling under bandages. It is essential that bandages remain intact and are not removed, for any reason. Failure to do so may result in loss of some of the correction and may require a secondary surgery.
Be sure to ask your plastic surgeon specific questions about what you can expect during your individual recovery period:
You will be given specific instructions that may include:
- Where will I be taken after my surgery is complete?
- What medication will I be given or prescribed after surgery?
- Will I have dressings/bandages after surgery? When will they be removed?
- Are stitches removed? When?
- When can I resume normal activity and exercise?
- When do I return for follow-up care?
The practice of medicine and surgery is not an exact science. Although good results are expected, there is no guarantee of complete satisfaction with the results. In some situations, it may not be possible to achieve optimal results with a single surgical procedure and another surgery may be necessary.
Ear Surgery Result
Ear surgery offers almost immediate results in cases of protruding ears, visible when the dressings that support the new shape of the ear during initial phases of healing are removed. With the ear permanently positioned closer to the head, surgical scars are either hidden behind the ear or well hidden within the natural creases of the ear.
The results of more extensive ear surgery and reconstruction may appear in stages over time.
